Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, choosing the right storage solution is crucial for businesses of all sizes. Microsoft Azure offers a plethora of storage options, each tailored to specific needs and use cases. This article aims to provide a detailed overview of the various storage solutions offered by Microsoft Azure, including their unique features, typical use cases, performance tiers, and how they compare to other Microsoft storage solutions like SharePoint and OneDrive. We will also explore the differences between Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS) storage solutions, along with their respective advantages and disadvantages. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of which Azure storage solution best fits your requirements. A section on best practices for choosing the right storage solutions has been included to further assist you in making an informed decision.
Understanding PaaS and SaaS Storage Solutions
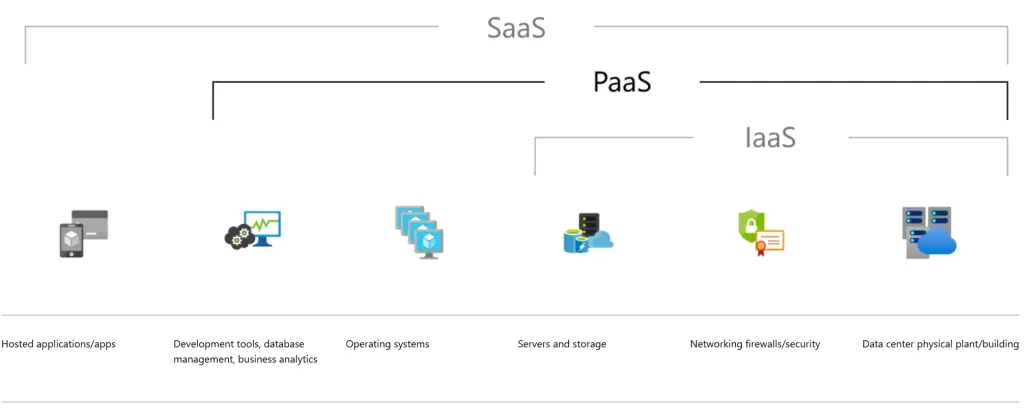
Before diving into the specific Azure storage solutions, it’s essential to understand the distinction between Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS) storage solutions. Azure primarily offers PaaS storage solutions, which provide a flexible and scalable platform for developers and IT professionals to build, deploy, and manage applications. This includes Azure Storage Accounts, which offer multiple storage options such as Blob Storage, Azure Files, Azure Queues, and Azure Tables. In contrast, Microsoft 365 offers SaaS storage solutions like SharePoint and OneDrive, which are fully managed storage solutions with built-in backup capabilities and redundancy.
PaaS Storage Solutions
PaaS storage solutions offer a high degree of flexibility and control, allowing businesses to customize and manage their storage infrastructure according to their specific needs. These solutions typically require more technical expertise to set up and maintain but offer greater scalability and integration with other services.
Advantages:
- High flexibility and control over storage infrastructure
- Scalable to meet growing data needs
- Integration with other cloud services and applications
Disadvantages:
- Requires technical expertise for setup and maintenance
- Potentially higher costs due to customization and management
SaaS Storage Solutions
SaaS storage solutions, such as SharePoint and OneDrive, provide a fully managed storage environment with minimal setup and maintenance requirements. These solutions are ideal for businesses looking for an easy-to-use, scalable storage option with built-in backup and redundancy features.
Advantages:
- Fully managed with minimal setup and maintenance required
- Built-in backup and redundancy
- Easy integration with other Microsoft 365 services
Disadvantages:
- Less flexibility and control over the storage infrastructure
- Limited customization options
Microsoft SaaS Storage Solutions
OneDrive
OneDrive is a cloud storage service that allows individuals and businesses to store files and access them from any device with an internet connection. It offers seamless integration with Microsoft Office and other Microsoft 365 applications, making it easy to share and collaborate on documents.
Features:
- Automatic backup and synchronization across devices
- Collaborative editing and sharing
- Integration with Microsoft Office applications
Typical Use Cases: Personal file storage, collaborative document editing, and backup for individual users.
SharePoint
SharePoint is a platform for creating, managing, and sharing content and applications across an organization. It provides a collaborative workspace where teams can work together on projects, share information, and manage documents.
Features:
- Document management and collaboration
- Intranet and team sites
- Integration with Microsoft 365 applications
Typical Use Cases: Enterprise content management, team collaboration, and intranet solutions.
Additional Microsoft SaaS Storage Solutions
Microsoft Teams: While primarily a communication and collaboration platform, Microsoft Teams also offers file storage and sharing capabilities integrated with OneDrive and SharePoint.
Microsoft Exchange Online: Offers email storage as part of the Microsoft 365 suite, with integrated archiving and compliance features.
Azure Storage Solutions
Azure Storage Accounts
Azure Storage Accounts offer a unified platform to manage various types of data, including blobs, files, queues, and tables. This section focuses on blob and file storage, detailing the performance tiers and options available for each and comparing general-purpose and premium storage accounts.
- Hot: Optimized for data that is accessed frequently, suitable for content distribution and streaming.
- Cool: Lower cost tier for data that is infrequently accessed and stored for at least 30 days, ideal for backup and archival storage.
- Cold: Cost-efficient storage for data that is infrequently accessed and stored for at least 90 days.
- Archive: Lowest-cost storage for data that is rarely accessed and stored for at least 180 days.
Customers can choose different tiers for individual blobs or containers within a general-purpose storage account, allowing for flexible and cost-effective data management.
- Premium: High-performance storage for I/O intensive workloads.
- Transaction optimized: Optimized for workloads that require high transaction rates.
- Hot: Optimized for data that is accessed frequently.
- Cool: Optimized for data that is infrequently accessed.
With file storage, customers typically pay a fixed price for reserving capacity, such as 1 TB, in contrast to blob storage where they only pay for what they use.
General-Purpose v2 vs. Premium Storage Accounts:
- General-Purpose v2 Storage Accounts: Offer a variety of storage services (blobs, files, queues, and tables) and support multiple performance tiers, providing flexibility and scalability for diverse workloads.
- Premium Storage Accounts: Designed for workloads requiring consistent high performance and low latency. These accounts typically support only block blobs and premium files, offering higher throughput and lower latency compared to general-purpose storage accounts.
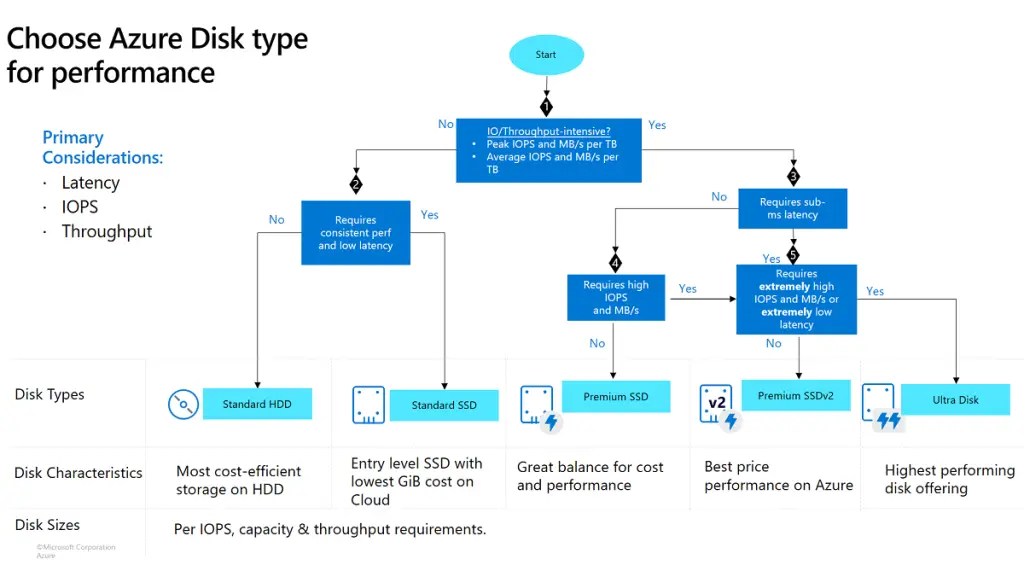
Azure Disk Storage
Azure Disk Storage provides high-performance, highly durable block storage designed for use with Azure Virtual Machines. It offers persistent, managed disks with enterprise-grade durability and performance. This solution is ideal for mission-critical applications requiring high throughput and low latency.
Performance Tiers:
- Standard HDD: Cost-effective storage option suitable for backup and infrequently accessed data.
- Standard SSD: Balanced performance and cost for general-purpose workloads.
- Premium SSD: High-performance storage for I/O-intensive applications.
- Premium SSD v2: Enhanced performance and scalability for demanding workloads.
- Ultra Disk: Ultra-high performance and sub-millisecond latency for the most demanding workloads.
Typical Use Cases: Database applications, enterprise applications, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), and data-intensive applications.
Azure Data Lake Storage
Azure Data Lake Storage is designed for big data analytics and allows you to store data of any size, shape, and speed. It provides a unified data repository for various data types and integrates seamlessly with Azure analytics services. The solution supports hierarchical file systems, making it easier to manage large datasets.
Performance Tiers:
- Hot: Optimized for data that is accessed frequently.
- Cool: Lower cost tier for data that is infrequently accessed and stored for at least 30 days.
- Archive: Lowest-cost storage for data that is rarely accessed and stored for at least 180 days.
Typical Use Cases: Data warehousing, machine learning, advanced analytics, and big data processing.
Azure NetApp Files
Azure NetApp Files is a powerful file storage service built for business-critical applications. It supports both NFS and SMB protocols and offers high throughput and low latency. The service provides various performance tiers to cater to different workload needs.
Performance Tiers:
- Standard: Suitable for general-purpose file services.
- Premium: High-performance storage for more demanding workloads.
- Ultra: Ultra-high performance for the most demanding applications.
Typical Use Cases: Enterprise applications, databases, high-performance computing, and large-scale file services.
Azure File Sync
Azure File Sync is a feature of Azure Storage accounts that centralizes your file shares in Azure Files while maintaining the flexibility, performance, and compatibility of an on-premises file server. It allows you to cache multiple Azure file shares on local Windows Servers, providing quick access to frequently used files. This solution helps organizations maintain local access to data while benefiting from cloud scalability and backups.
Typical Use Cases: Hybrid storage solutions, centralized file management, and cloud backup for local file servers.
Azure Stack Edge
Azure Stack Edge is a cloud-managed device that brings Azure’s capabilities to the edge of your network. It provides local compute and storage to handle large data volumes generated at the edge and processes data before sending it to Azure. This solution is particularly beneficial for scenarios that require immediate data processing.
Typical Use Cases: IoT solutions, edge computing, remote locations with limited connectivity, and machine learning at the edge.
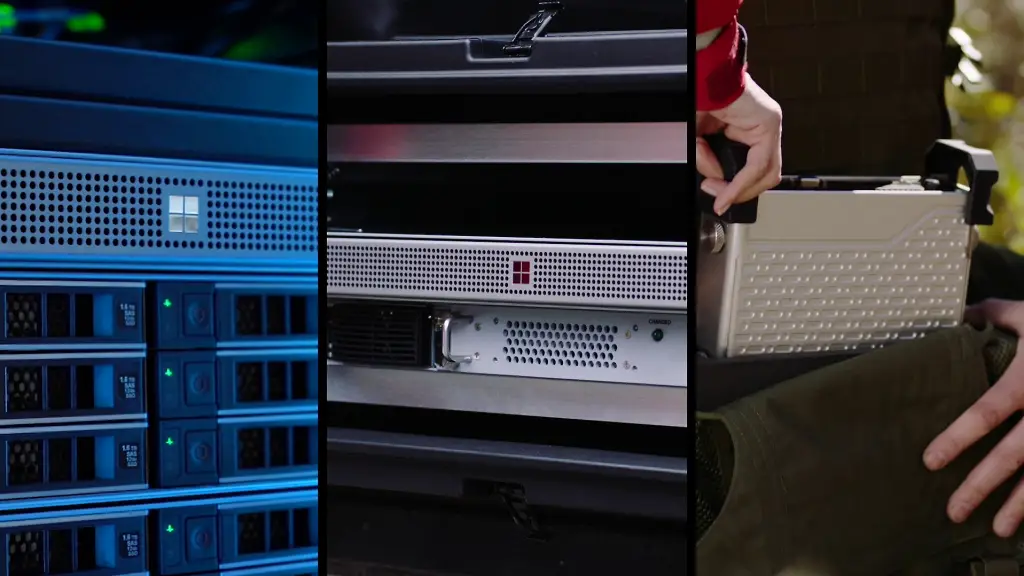

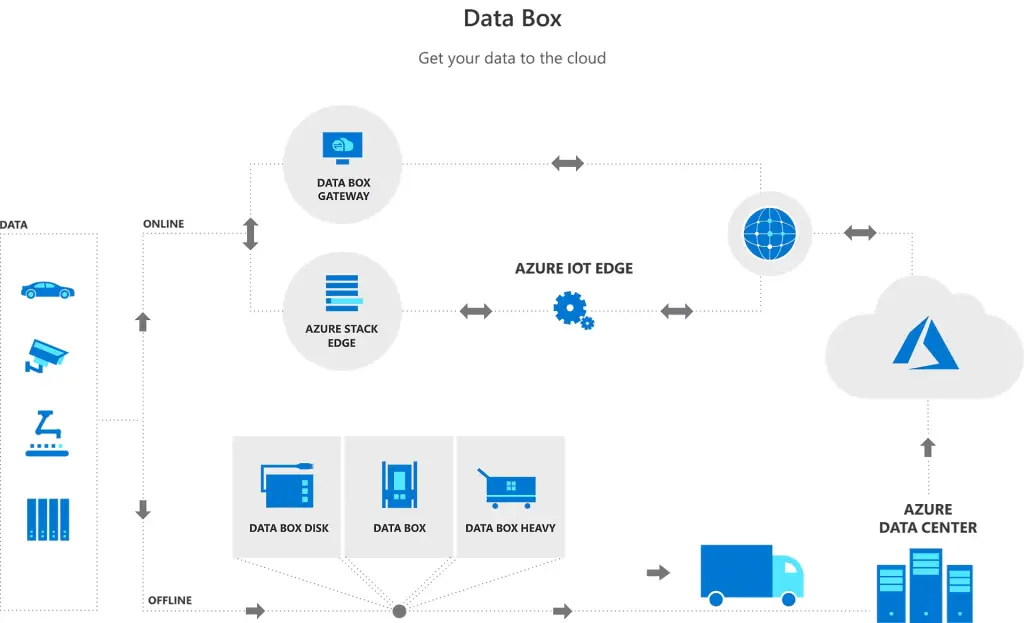
Azure Data Box
Azure Data Box products help you move large amounts of data to Azure when network constraints make uploading data impractical. These physical devices are designed for secure data transfer to Azure. Azure Data Box can be used for data center migration, disaster recovery, and content distribution. It ensures that large datasets can be efficiently and securely transported to Azure for further processing.
Typical Use Cases: Data center migration, disaster recovery, and content distribution.
Azure Elastic SAN
Azure Elastic SAN provides scalable and high-performance storage for enterprise workloads. It is designed to meet the needs of applications requiring consistent performance and high availability. This solution supports various performance levels, allowing businesses to tailor storage to their specific requirements.
Performance Tiers:
- Different levels: Various performance configurations to meet diverse workload needs.
Typical Use Cases: ERP systems, large databases, and applications requiring consistent performance and high availability.
Azure Container Storage
Azure Container Storage offers persistent storage for containerized applications. It integrates with Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) and provides dynamic provisioning of storage resources. This ensures that containerized applications have the necessary storage resources available on-demand.
Typical Use Cases: Containerized microservices, DevOps workflows, and stateful applications in containers.
Azure Storage Actions
Azure Storage Actions automate tasks and workflows using Azure Logic Apps and Azure Functions. This service can handle various storage-related tasks, such as moving data between storage accounts, managing backups, and processing storage events.
Typical Use Cases: Data management, backup automation, and processing storage events.
Comparison of Azure Storage Solutions
Solution | Type | Protocol | Performance Tiers | Use Cases | Key Features |
Azure Disk Storage | Block Storage | SCSI | Standard HDD, Standard SSD, Premium SSD, Ultra Disk | VMs, Databases, Enterprise Applications, VDI | High throughput, Low latency |
Azure Blob Storage | Object Storage | HTTP/HTTPS | Premium, Hot, Cool, Cold, Archive | Content Distribution, Streaming, Backup, Archive | Scalable, Unstructured data |
Azure Data Lake Storage | Big Data Storage | HDFS, REST | Hot, Cool, Archive | Analytics, Machine Learning, Big Data Processing | Scalable, Integrates with analytics services |
Azure Files | File Storage | SMB | Standard, Premium | File Shares, Lift-and-Shift, Company-wide Storage | Fully managed, Cross-platform |
Azure NetApp Files | File Storage | NFS, SMB | Standard, Premium, Ultra | Enterprise Applications, Databases, HPC | High performance, Low latency |
Azure File Sync | File Sync | SMB | Depends on Azure File Tier | Hybrid Storage, Centralized File Management, Cloud Backup | Centralized, Scalable |
Azure Stack Edge | Edge Device | N/A | N/A | IoT, Edge Computing, Remote Locations | Local compute, Data processing |
Azure Data Box | Data Transfer | USB, Network | N/A | Migration, DR, Content Distribution | Physical device, Secure |
Azure Elastic SAN | Block Storage | iSCSI | Different levels | ERP Systems, Databases, Enterprise Workloads | Scalable, High availability |
Azure Container Storage | Persistent Storage | SCSI | N/A | Containerized Applications, DevOps Workflows | Dynamic provisioning, Managed |
Azure Storage Actions | Automation | HTTP/HTTPS | N/A | Task Automation | Logic Apps, Functions |
Best Practices for Choosing the Right Storage Solution
Choosing the right storage solution can be a daunting task, given the variety of options available. However, following some best practices can help streamline the process and ensure that you select the most suitable storage solution for your needs. This section outlines key strategies to guide you in making an informed decision.
- Understand your workload requirements: Assess the performance, capacity, and durability needs of your applications.
- Evaluate cost vs. performance: Choose a performance tier that balances your budget with your performance requirements.
- Leverage hybrid solutions: Integrate on-premises and cloud storage to maximize flexibility and control.
- Plan for scalability: Ensure the solution you choose can scale with your growing data needs.
Limitations
While Microsoft Azure offers a wide range of storage solutions, there are some limitations to consider:
- Cost: Depending on the performance tier and data volume, costs can escalate.
- Latency: For applications requiring real-time data access, latency can be a consideration, although Azure offers solutions to mitigate this.
- Complexity: Setting up and managing some of the more advanced solutions can require significant technical expertise.
Conclusion
Choosing the right Azure storage solution depends on your specific needs and use cases. From high-performance block storage to scalable object storage and hybrid solutions, Microsoft Azure offers a comprehensive suite of storage options to meet diverse business requirements. By understanding the unique features, performance tiers, and use cases of each solution, you can make an informed decision and leverage the full potential of Azure’s storage capabilities. For detailed documentation on each product, please refer to the corresponding product website.